Hello 🙂 !
Aujourd’hui nous allons voir comment paramétrer un Storage pool dans un environnement Windows Server 2012.
Présentation du Storage Pool:
La notion de Storage Pool est une nouvelle fonctionnalité présente depuis Windows Serveur 2012.
L’objectif de cette fonctionnalité est de pouvoir regrouper plusieurs disques physiques en un seul volume logique.
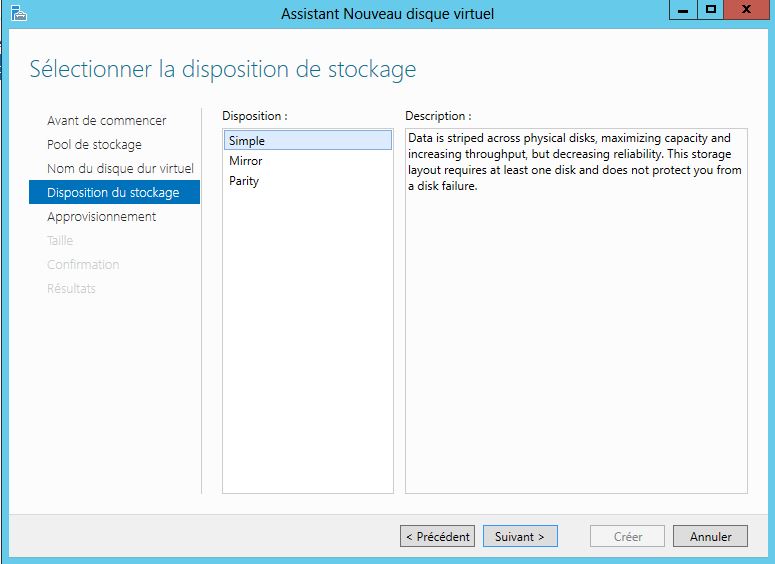
Il est ainsi possible de pouvoir mettre en place des scénarii de stockage en place:
- RAID 0 (Stripping en anglais) : Pas de redondance
- RAID 1 : Disques en mirroir
- RAID 5 : Volumes agrégé avec de la parité
Cette fonctionnalité de Storage Pool peut etre exploité via la mise en place d’une plateforme de virtualisation: Hyper-V
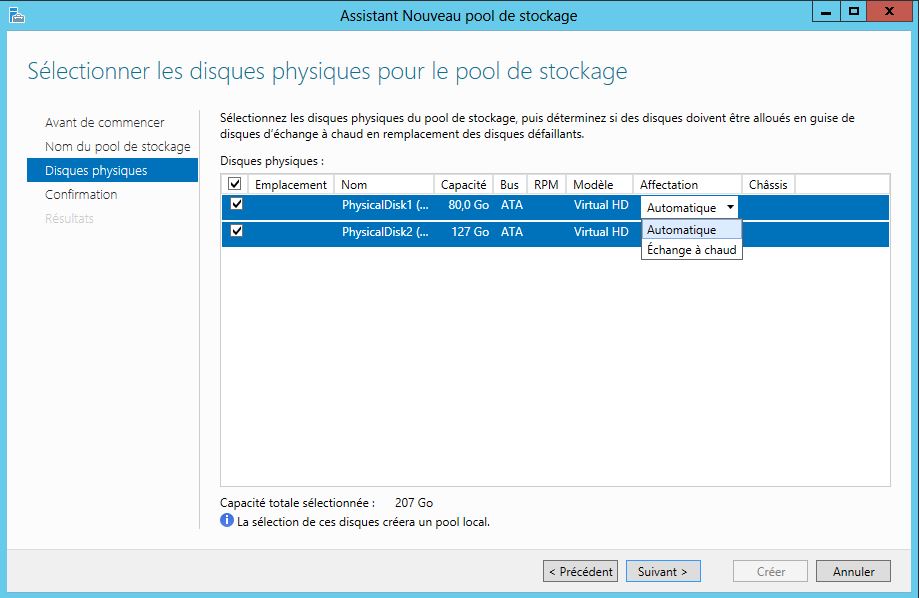
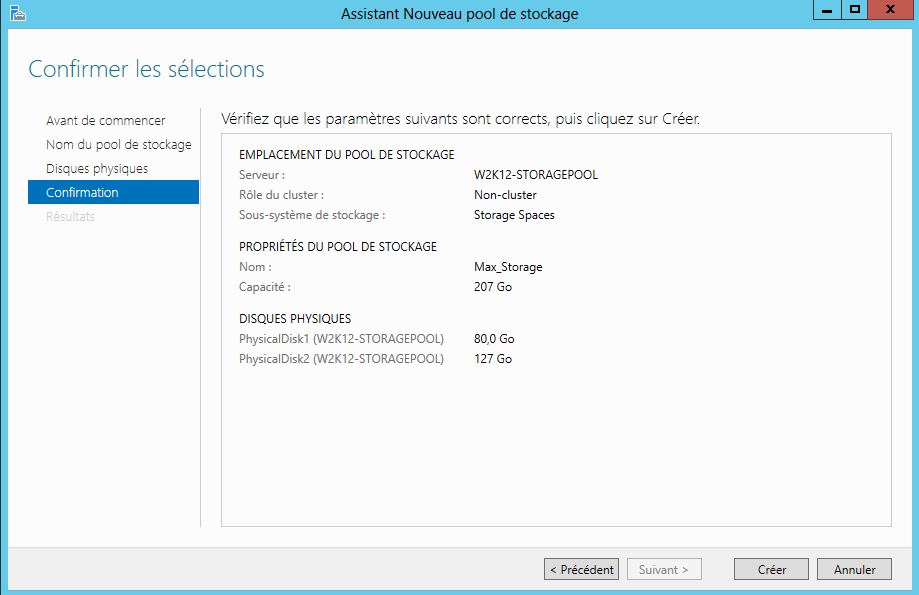
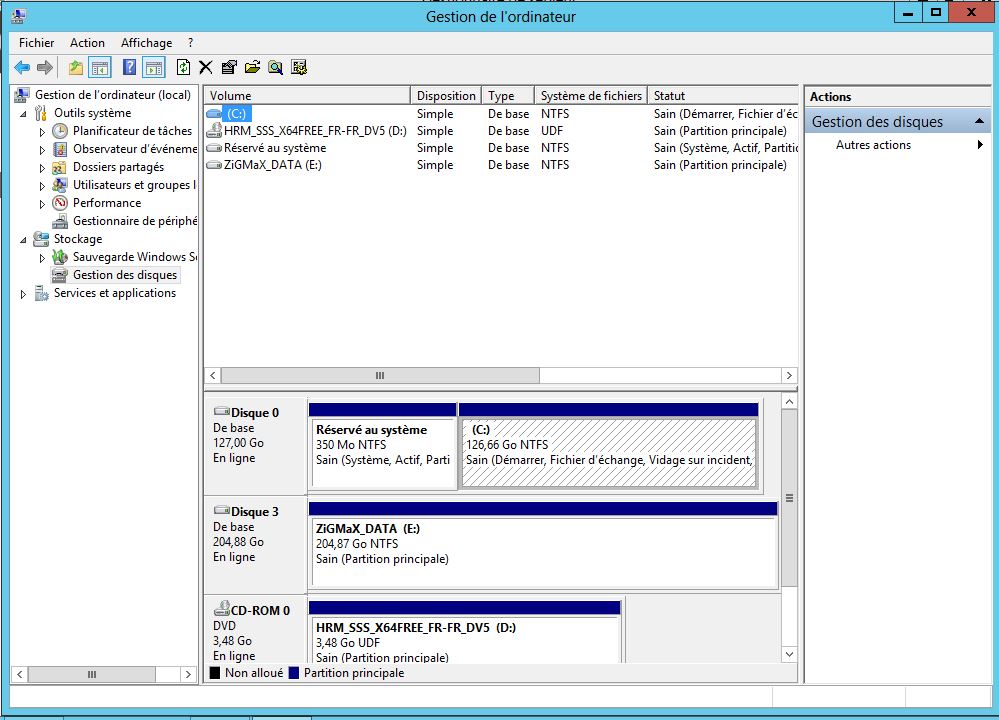
Configuration de mon serveur:
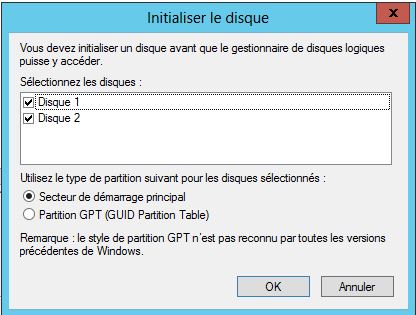
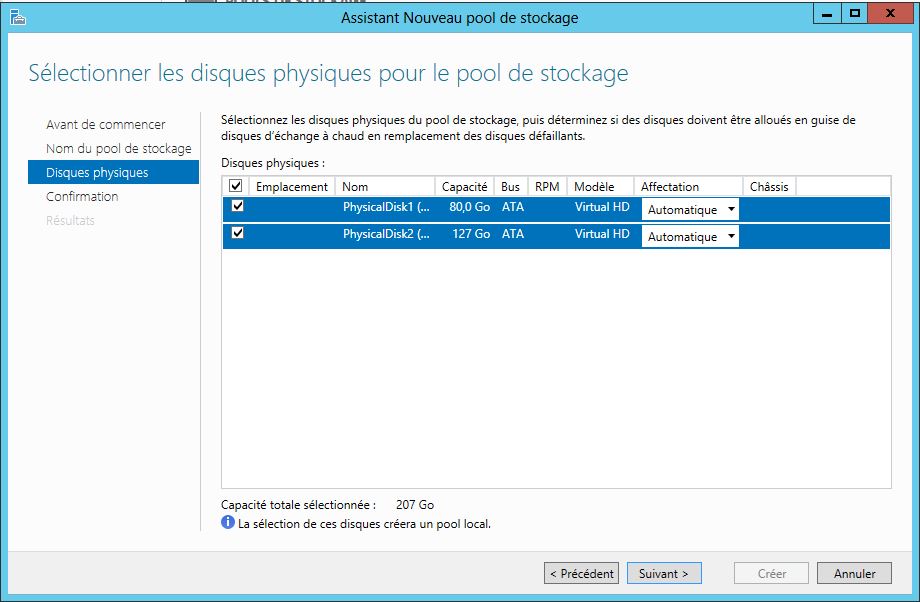
- 1 HDD Système: 80 Go
- 1 HDD 80 Go
- 1 HDD 120 Go
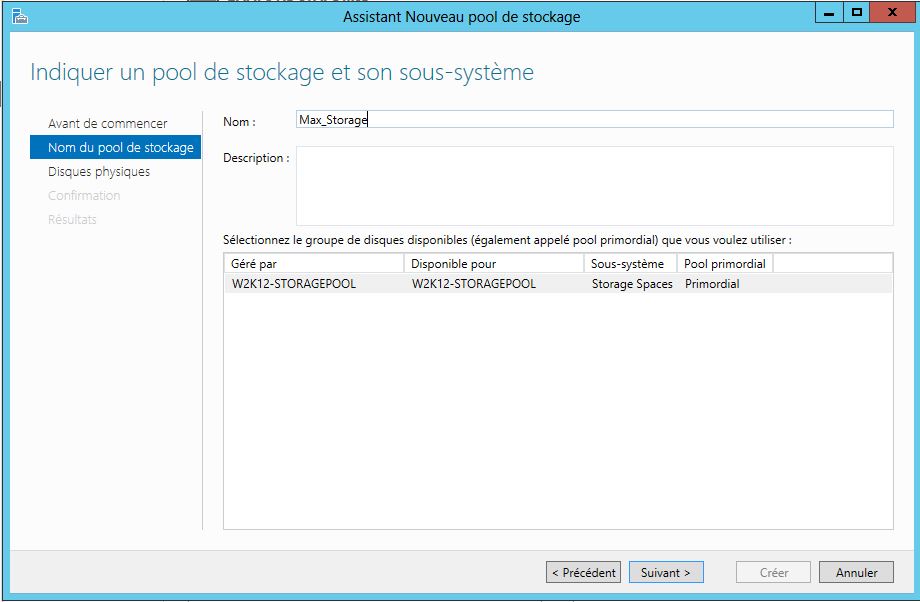
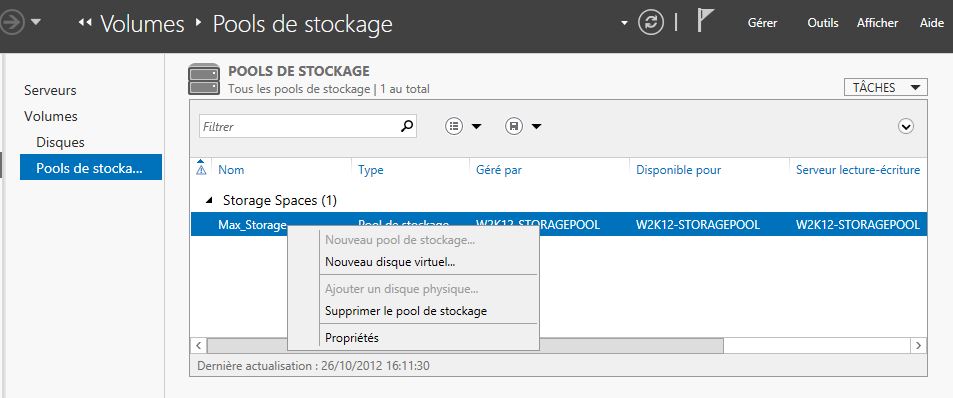
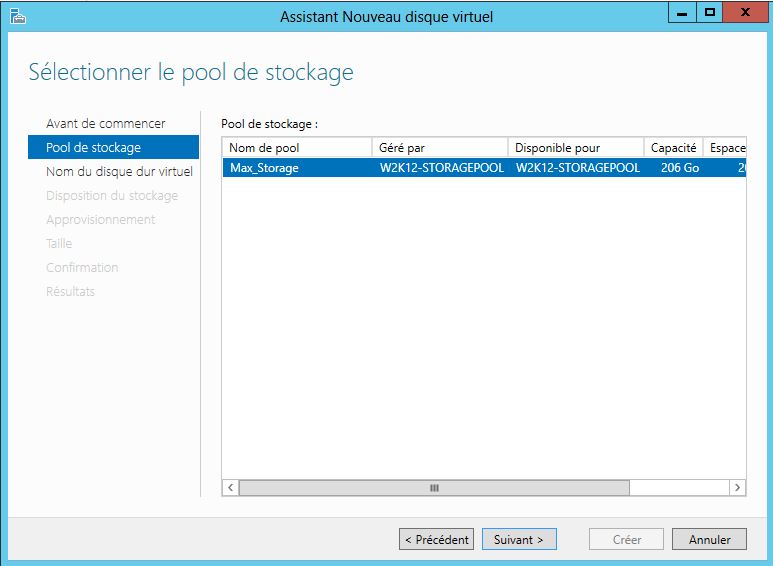
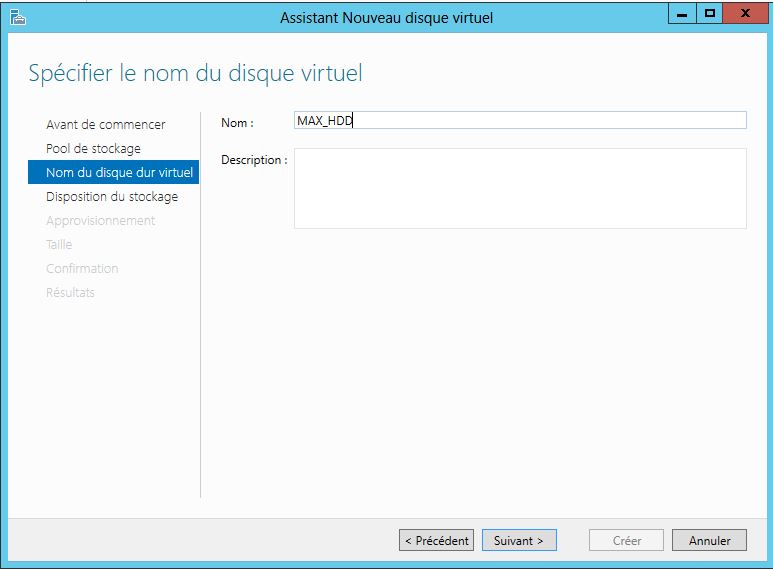
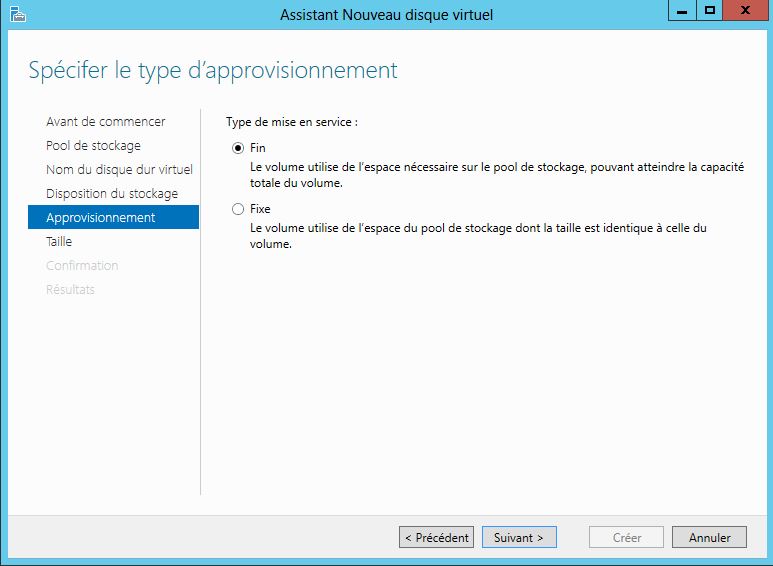
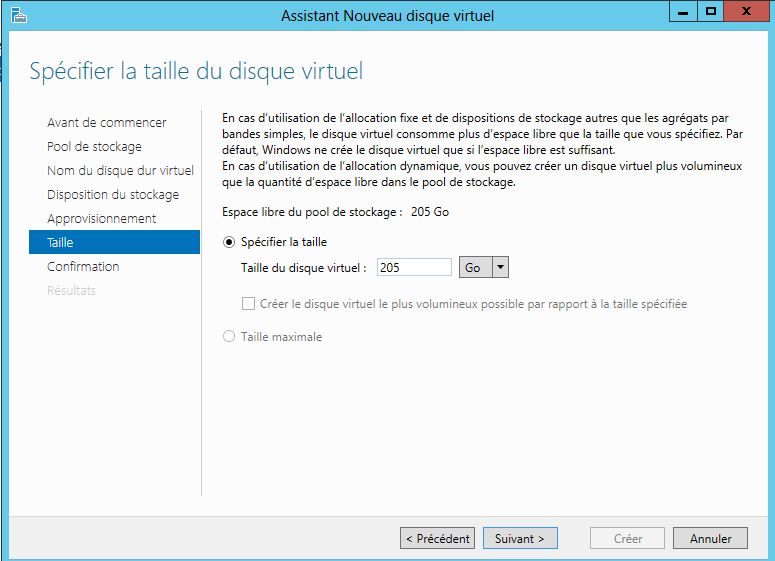
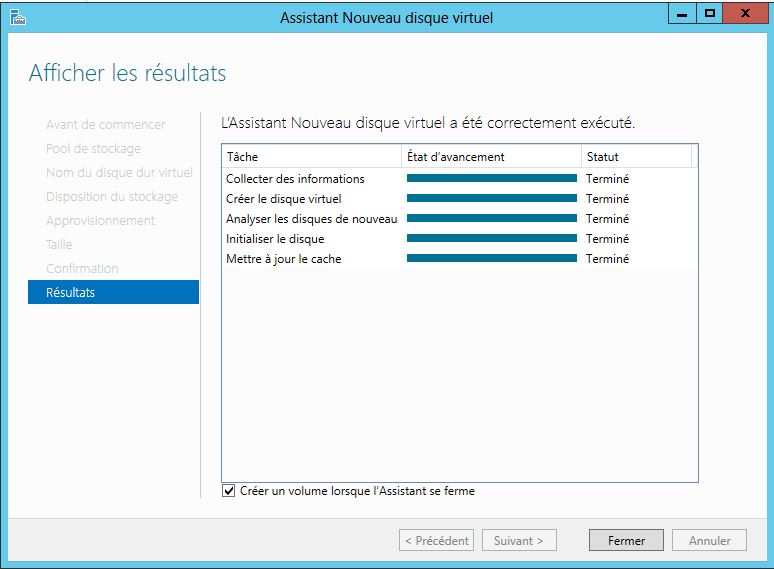
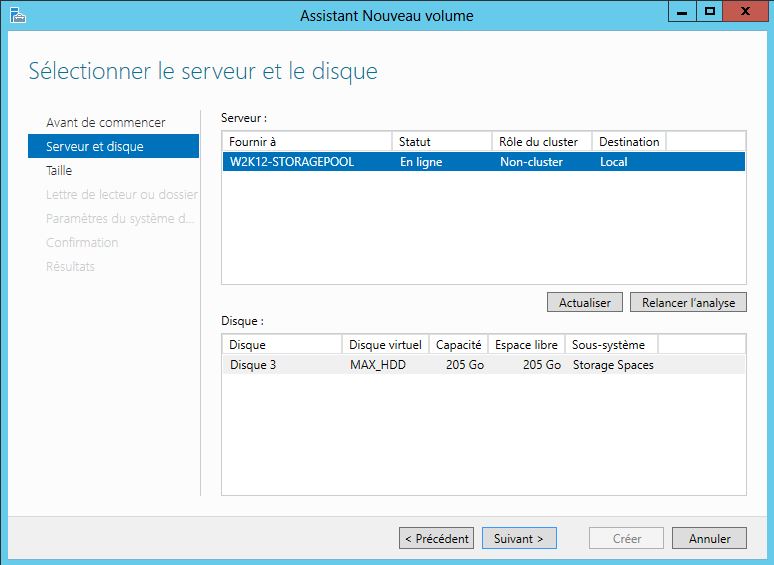
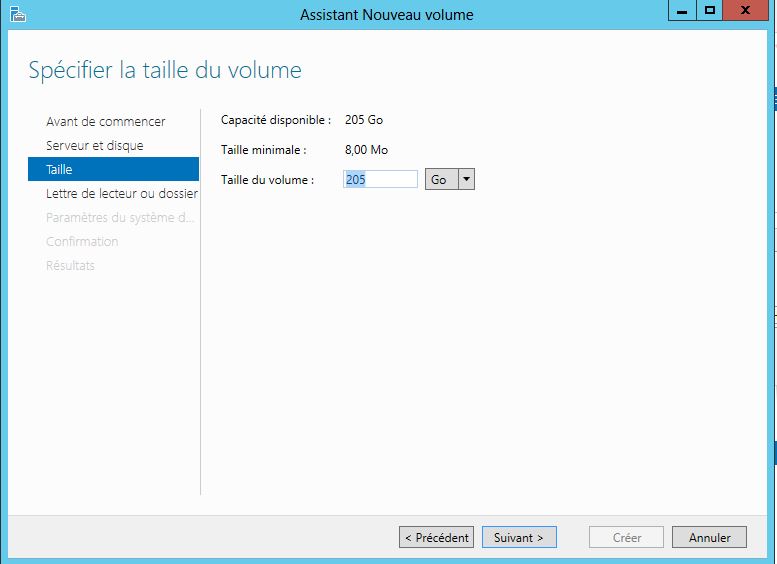
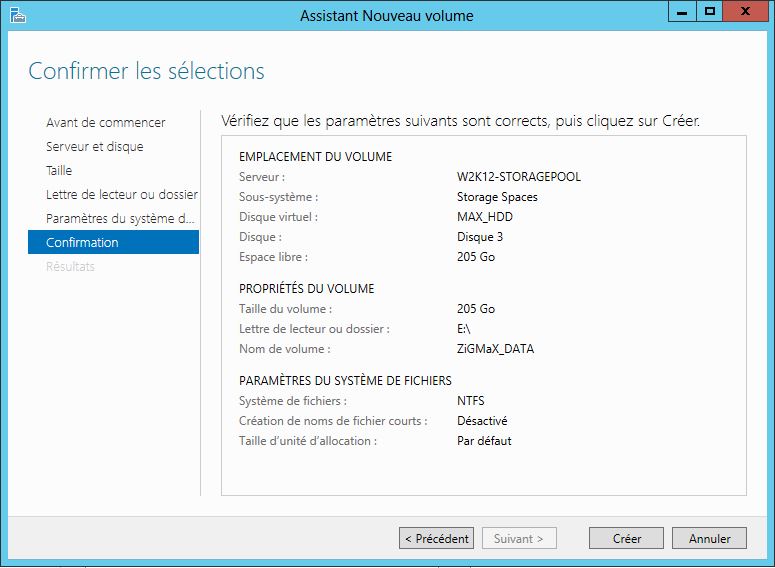
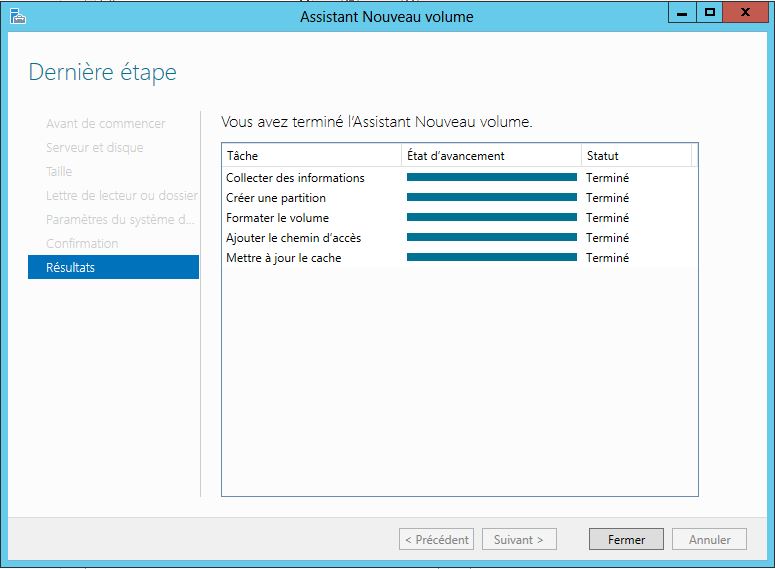
Mise en place:
Sources: